Because the requirements for the detection,
monitoring, and transformation of environmental constituents are increasing at
a significant rate developing sensor interfaces must be sensitive to low level
exposures and have fast response times. As concerns about the impact of gases
on health and environmental concerns increase, the reliable detection of
several gases over a range of temperatures has become a priority. Included inthis group, NOx associated with air pollution, combustion, and respiratorydisease is critical. NO is the primary monitor of an asthmatic attack and can
also provide rapidly accessed noninvasive disease detection. NH3, which plays
an especially important role in urban environments, also is produced albeit at
much lower levels, during an asthma attack.
SOx and H2S as well as NOx play an
important role in automotive and industrial exhaust, acid rain, photochemical
smog, and corrosion and natural gas venting.. PH3 is an extremely toxic gas
used for fumigation in agriculture and is a byproduct in the production of
methamphetamines. Advances in gas sensor technology used to monitor theseexemplary gases have been driven by sensitivity, selectivity, stability,response time, and durability. Here, we review a new solid-state device
technology which detects analytes by measuring an electrical property of a
detection interface and from this measurement we can evaluate an interacting
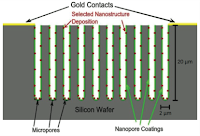
gas. Conductometric gas sensors can be made to consist of a sensitive interface
layer decorated by nanostructure island sites.
No comments:
Post a Comment