 |
| Spiro-indolinone |
From the result of p53-MDM2 complex crystal structure, tryptophan
residues on the indole ring of p53 is the most critical binding element for p53
binding MDM2 protein, which was buried in the hydrophobic pocket, and indole on
the NH and MDM2 formed a hydrogen bond. Wang and his team members used
computer-assisted drug screening to find compounds that mimic the indole ring
and found that the structural properties of 2-indolinone were most consistent
with that of indole. 6-chloro-2-indolinone was identified as a predominant
fragment on the basis of previous work on peptide compounds and Nutlin (Trp
pocket with key chlorine atoms capable of occupying MDM2 protein). The Spiro
cyclic backbone provides the necessary platform for introducing side chains so
that the hydrophobic side chains can be inserted into Leu and Phe pockets. The
crystal structures of the resulting compounds MI-63 and MDM2 were recently
reported by Popowicz et al. Read more>>>>>>>>>
 |
| Micro/Nano Plastics |
Given that plastic polymers are highly resistant to degradation, the
influx of these persistent, complex materials is a risk to human and
environmental health. Microplastics is described as a truly heterogeneous
mixture of particles ranging in size form a few microns to several millimeters
in diameter; including particles of various shapes from completely spherical to
elongated fibers. Microplastic pollution has been reported on a global scale
from the poles to the equator. The main route of concern is currently as a
consequence of ingestion, which could lead to physical and toxicological
effects on aquatic organisms. To this end, in order to minimize the negative
impacts posed by plastic pollution (microplastics), a plethora of strategies
have been developed at various levels to reduce and manage the plastic wastes.
The main objective of this paper is to review some of the published literatures
on management measures of plastic wastes. Read more>>>>>>>
About defence
system of vertebrate, the complexed problems of developing our dual system, the
innate and inductive do not seem to guard or even protect the maturation of one
internal threat to survival. Also, all the individual suffers from the risk of immunodeficiencyin daily activities with both internal and/or externals events, such personalhabitat of individual, such in lifestyle related disease. Recently,
complementary, and alternative medicines (CAM) have interested more and more
attractive since they are able to treat many life-style related diseases, such
as Diabetes mellitus, fatigue syndrome that spurred in the industrialized
world. The present report had showed that typical styles of CAM, preparing
special molecule for both digestive and easy to augmented human complement
component that regulated the functions of leukocytes in human immune defence
system.

We had been published and proposed that the health promoting supplement
could work after depredated the polysaccharide to appropriate fragment they
possible to activate complement component. This was especially being part of
alternative complement pathway. Dietary Supplements and fermented derivatives
suggested as potent agent food supplement for regulating an acquired immunity
through alternative complement pathway. These processes were close
concollection of the complement activating process different from invasion of
infectious agent where the immune complex and/or toxic polysaccharide such as
LPS worked as pathway of complement.(Read More)
The advent of
targeted therapies, i.e., small molecules or antibodies that interfere with
signaling proteins involved in the etiology of cancer, revolutionized thetreatment of tumors with an addiction to specific oncogenes (e.g., ALK in lung
cancer, Bcr-Abl in chronic myeloid leukemia, KIT in GIST, EGFR in lung cancer,
HER2 in breast cancer or MET in liver tumors). However, for many cancers, the
progressionfree survival of patients treated with targeted therapy is less than
one year, which justify for a regain of interest in cytotoxic agents including
metallodrugs.

Indeed, the prevalent success of cisplatin in the treatment of
various types of cancers has placed organometallic compounds on the forefront
in the development of anticancer drugs. In this quest, copper derivatives hold
promising opportunities due to opportunities provided by the hypoxic
environment that is a hallmark of cancer cells coupled with the ability of
copper complexes to catalyze the formation of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen
species (ROS and RNS).(Read More)
Such known
programs as Lukas Program, ThermoCalc, ChemSage, FACTSage, MTDATA, PanEngine,
PANDAT are created for the calculations of phase equilibria. Thanks to them itbecame possible the use of more realistic models of the thermodynamicproperties of phases, the calculation of phase diagrams in the complex
two-component systems and the systems with the large number of components. The
CALPHAD-method, which makes possible to generalize and to refine within the
framework information about the phase equilibria and the thermodynamics of
phases for one model, is most claimed today. It is effective means for
decreasing the volumes of the experiments, necessary for understanding of phase
transformations in the alloys and the ceramics. The CALPHAD ideology became the
powerful means of theoretical studies and obtaining of adequate information
about the phase equilibria.

Thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams for the
technologically important multi-component materials can be predicted with its
use. The reliable thermodynamic descriptions of two-component systems are the
basis of the data bases with such characteristics. However, the CALPHAD
application is limited by a deficiency in reliable thermodynamic data and the
weak possibilities of the visualization of three-dimensional objects. In
addition to this, using of thermodynamic methods of the states diagram
calculating is hindered by the need of evaluating the thermodynamic properties
of phases (in the absence of experimental data) and the agreement of
experimental data of phase equilibria with the thermodynamic models. The
innovation technology of assembling the space models of multidimensional phase
diagrams from the entire totality of the geometric images corresponding to them
is proposed: “To decode the diagrams topology the schemes of uni- and invariant
states had been elaborated. This sort of schemes with phase’s routes
designations makes possible to calculate the number of phase regions, surfaces
and to know a type of every surface (plane, ruled or unruled surface). Detailed
analysis of T-x-y diagrams geometrical constructions had been carried out with
their aid, and their computer models had been designed” .(Read more)
In
the last decades, the use of agrochemicals has been a common practice in
intense agriculture, which has considerably increased pollution problems of
surface and ground water. Oxyfluorfen
[2-chloro-1-(3-ethoxy-4-nitrophenoxy)-4-(trifluromethyl)-benzene], a member of
the herbicide class nitrodiphenyl ether, has a high degree of weed control and
great versatility of application. Oxyfluorfen is considered to be highly resistant
to degradation in water. And has Potential adverse effects on the ecosystemeven if present at very low concentration levels, where the half-life of
oxyfluorfen ranged from 72 to 160 days for water. Many conventional methods
have been successfully applied for the efficient removal of oxyfluorfen from water
sources such as adsorption, advanced oxidation, photo Fenton, UV/H2O2
, and biological treatment.

In recent years novel methods for water
purification have been developed including chemical, electrochemical and
photochemical processes. In this scenario, the electrocoagulation (EC) is an
electrochemical has attracted increasing interest as a promising powerful
method for efficiently removing pesticides from water such as Malathion, methyl
parathion, atrazine and triazophos, imidacloprid and chlorpyrifos, and 2,4-
dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (2,4-D).The
aim of this study is to conduct an experimental investigation on the removal of
a oxyfluorfen and COD from the aqueous solution using the electrocoagulation
method. and to investigate the kinetic and adsorption isotherm studies on the
removal efficiency.(Read more)
The
toxicity of free heme has been documented in several disease types. For
example, in hemolytic anemias such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia, release of heme from hemoglobin followinglysis of red blood cells is known to cause cell death. In a critical care
situation such as hemorrhagic injury, neuronal cell death is caused by the
lysis of red blood cells, which release hemoglobin and its breakdown product
hemin. Physiological levels of free heme in the blood are maintained at low
levels (0.1 -1 μM) by the high binding affinity of proteins such as serum albumin,
hemopexin and haptoglobin. When internalized, free heme is catabolized by heme
oxygenases (HO1 and HO2 isoforms) and therefore the amount of cellular damage
free heme produces is limited by the stress-responsive HO1 isoform.

In addition
to HO1 and HO2 isoform regulated cellular damage, the oxidative state of iron
(from Fe2+ to Fe3+ via the Fenton reaction) within heme
can produce harmful superoxide free radicals in the brain that can lead to
oxidative stress, initiation of lipid peroxidation and neuronal death.Pathological
conditions can increase the level of heme and iron. For example in acute
conditions such as severe hemolytic crisis in sickle cell disease,
heme levels can increase up to 20 μM or to greater than 200 μM (supraphysiological
levels) in thalassemia. Therefore, further studies on the cross talk between
neuroinflammatory mediators and iron-containing hemoproteins such as hemin are
warranted.(Read more)
Though enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) is a
standard technology for removing phosphorus from wastewater, the responsible
organisms and relevant mechanisms are complex and not well-understood.
Substrate type has been identified as an important factor affecting the
competition between polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) and
glycogen accumulating organisms (GAOs), which are usually dominant in a failedEBPR. In addition, temperature is also considered an important factor in
practice governing the efficiency of phosphate removal in EBPR because the
population competition between PAOs and GAO s is significantly
Ref. affected by water temperature. Ref.found that the predominant microbial
population changed from PAO s to GAO s when temperature
gradually rose from 20°C to 35°C. Similarly found PAOs were the
dominant microorganisms at low temperature (10°C), regardless of the influent
carbon source or pH.

However found conflicting results. Heavy metal ions have
also been reported to be able to inhibit biological reactions responsible for
carbon, nitrogen and phosphate removals. Ref.found that the presence of Cd (II)
significantly changed the structure of microbial population and was toxic to
the bacterial community in nutrient removal sludge, especially to the bacteria
in the Beta proteobacteria. Monitoring of a full-scale advanced municipal
wastewater treatment plant showed the P removal efficiency decreased
dramatically after tin (Sn) levels in the solids fraction of the mixed liquid
suspended solids (MLSS) exceeded 4 μgSn L-1 . A similar study by showed
2 mg L-1 of Cd(II) took the lead in affecting biological phosphate
removal. At the level of 5 mg L-1 of Cd (II), the total nitrogen
removal and nitrification efficiency substantially declined and the denitrification
rate was inhibited by about 61%. At the same time, the inhibition percentages
of anaerobic release, anoxic and aerobic uptake rates of phosphate were about
76, 64, and 90%, respectively Ref.Further conducted a series of batch
experiments to identify the toxic effects of Pb(II), Ni(II) and Cd(II) on
nitrification and denitrification for nutrient removal sludges.(Read more)
Bioethanol of first generation can be produced by the
fermentation of plants containing sugar and starch. Whereas second generationbioethanol can be produced through hydrolysis and subsequent fermentation ofcellulose. Then, this second type do not compete directly with food crops for
land use since it can be obtained from a wider range of feedstocks
(agricultural residues, woody raw materials or energy crops). However,
currently wheat is still the main crop for bioethanol production. Shows global
ethanol production by different countries from 2007 to 2015.

It can be observed
that the values peaked in 2015 after a dip in 2011 and 2012. Moreover, it
indicates that the countries with the highest production and USA and Brazil. The
bioethanol production process depends on the feedstock, going from the simple
conversion of sugars by fermentation, to the multi-stage conversion of lignocellulosic
biomass into ethanol. Moreover, some thermochemical processes have been
analyzed to produce bio-ethanol: gasification followed either by fermentation ,
or by a catalyzed reaction.(Read more)
Process design and optimization are fundamental steps to
ensure the economic sustainability of chemical processes. Suitable description
of the performance of the various unit operations of the plant should be made
and integrated, to understand the mutual interferences both under steady state
conditions and under unsteady operation. Process simulation tools are helpfulto compute both situations. The stationary case can be simulated with packages
dealing with material and energy balances applied to each unit and extended to
the whole plant.

More complex is the unsteady state case, which needs dynamic
modelling to describe the time-dependent evolution of the system. Separation
equipment are simulated using algorithms embedded in process simulators, which
may be more or less complex and adequate to represent the system with the
desired approximation. A key issue in this case is the correct choice of a thermodynamic
package able to cope with the system complexity in sufficient detail, in order
to make reliable previsions on phase equilibria and components partition among
them.(Read more)
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most important
neurodegenerative disorder in the elderly population, after Alzheimer’sdisease. With a prevalence ranging from 35.8 per 100,000 to 12,500 per 100,000
and annual incidence estimates ranging from 1.5 per 100,000 to 346 per 100,000
in different countries, PD represents today a major age-related problem of
health. Meta-analysis of the world wide data indicates a rising prevalence of
PD with age (from 41 per 100,000 at 40-49 years to 1,903 per 100,000 at over
age 80).

PD also shows a characteristic distribution by geographic location (a
prevalence of 1,601 per 100,000 in patients from North America, Europe and
Australia, and a prevalence of 646 per 100,000 in Asian patients). PD is more
prevalent in males (1,729 per 100,000, >65 yrs) than in females (1,644 per
100,000), with a peak prevalence in the age group of ≥ 90 years (4,633 cases
per 100,000), and a mean prevalence of 1,680 per 100,000 in people older than
65 years of age. Prevalence and incidence Male/Female ratios increase by 0.05
and 0.14, respectively, per 10 years of age. Incidence is similar in men and
women under 50 years (M/F ratio <1.2), and over 1.6 times higher in men than
women over 80 years [8].(Read more)
We are witnessing the major improvements of
mass spectrometry that are taking places both in the structural analyses of NPs
but also in the mass elucidation of NPs. The advances are mainly coming in the form
of improvements in instruments such as advances in ion sources.(Read more)
Tridax
procumbens Linn belongs to the family asteraceae. The extracts of Tridax
procumbens have been used as indigenous medicine for a variety of
ailments. It has been extensively used in Indian traditional medicine for wound
healing, as anticoagulant, antifungal and insect repellent, in diarrhea and
dysentery. Leaf extracts are used to treat infectious skin diseases in folk
medicines. It is also dispensed as ‘Bhringraj’ which is well known ayurvedicmedicine for liver disorders.

Antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and
immune modulatory properties have also been demonstrated. Plants have strong
ability to synthesize aromatic substances, most of which are phenols or their
oxygen substituted derivatives which are mostly secondary metabolites. At least
12,000 have been isolated, a number estimated to be less than 10% of the total.
These substances serve as plant defense mechanisms against predation by
microbes, insects, herbivores. Some terpenoids are plant pigment, some are
plant flavoring agents and some are having medicinal properties.(Read more)
In the systems far from equilibrium the procedure of a
chemical reaction between the components does not always correspond to the
macroscopic equations. The elementary act of collision of the components and
the nature of the reaction products being formed depend on the energy of the
colliding molecules, on their correct spatial orientation. Collision of the
initial components and formation of the reaction products are proportional to
the motive force of the process which is normally perceived as affinity.
According to de Donder, affinity is determined by the relationship of chemical
potentials of substances undergoing a chemical reaction.

If several reactions
proceed in the system, affinity and transformations of the components must be
determined separately for each reaction. In the chemical reaction at the
bifurcation point, the system loses stability, and passes to a nonequilibrium
state, which makes it possible to assume a new quality of evolution of the
dynamic system. There takes place a change in the nature of motion and
structure of the system. When the system moves to the bifurcation point, an
important role is played by the chemical potential and affinity of the system.(Read more)
Recent preclinical and clinical studies have shown that
vascular calcification is inexorable pathological process leading to mechanical
rigidity and stiffness of vascular wall, endothelial dysfunction, development
and accelerating atherosclerosis even in the absence of established
cardiovascular (CV) disease.
Ectopic calcification is represented by several
mutually counteracting molecular mechanisms, i.e., oxidative stress,
microvascular inflammation, immune cell-to-cell cooperation, accumulation of
lipids and extracellular proteins, vascular reparative systems, and metabolic disorders.
All these processes are under tight regulation of vitamin D, parathyroid
hormone-related peptides (fibroblast growth factor, transcription factor Sox2,
betacatenin, etc.) and matricellular proteins such as osteopontin (OPN) and
phosphate.(Read more)
Plastic pollution has been
a menace to our society for decades due to continued rise in human population
combined with consumption, degradation through abiotic and oceanic factors
(fragmentation due to Ultraviolet radiation, mechanical abrasion) and their
wide applications in every human endeavours; packaging, agriculture,
automobiles, biomedical, telecommunication, building and construction,
furniture, plumbing works, transportation, etc.This is clearly evident in the
Great Pacific Garbage Patch, a ring of marine litter, containing large amount
of plastic wastes, in the central North Pacific Ocean located between 135-155°W
and 35-42°N .

Plastics are still in high demand in this modern era to improve
the quality of life but undoubtedly have changed the way we live. In coastal
areas, the marine pollution of plastic is increasing at alarming rate due to
indiscriminate disposal by the consumers (beach visitors, tourists,
shipping/maritime companies, fishery operators, etc.). Records have shown that
on a global scale, over 300 million metric tons of plastics are produced
annually out of which 50% of this are disposed indiscriminately into the
environment and about 4.8-12.7 million tons end up in marine ecosystem (water
column, sediment and biological tissues) as microplastics (plastic materials
<5mm), arising from degradation of larger plastic litter. (Read more)
Coumarin family considered an essential heterocyclic compounds which belong to benzopyrones family that contains of phenyl ring fused with a pyrone ring. Coumarin classified into six groups count on chemical structure of compounds and these group are simple (coumarins, bi coumarins, phenyl coumarins, pyrano coumarins, furano coumarins and dihydrofurano coumarins)Coumarin mainly existed in plant kingdom such as (leaves, roots, stems and fruits). Besides, they found in different oils as ‘’lavender oil, cinnamon bark, oil and cassia oil’’.
 Moreover, coumarin derivatives have changed uses such as ‘’optical brightening agents, laser dyes, cosmetic industry agrochemical industries and food additives’’. Furthermore, Coumarin derivatives have important biological activity as antibacterial, antifungal, anti-oxidant, anti-allergic, antiinflammatory, anti-thrombotic, hepatoprotective, anti-viral, anticarcinogenic activities. So, this study involved the biological estimation of N’-(3-(hydroxyimino) butan-2-ylidene)-2-oxo-2Hchromene- 3-carbohydrazide (H2L) and its metal complexes.
Moreover, coumarin derivatives have changed uses such as ‘’optical brightening agents, laser dyes, cosmetic industry agrochemical industries and food additives’’. Furthermore, Coumarin derivatives have important biological activity as antibacterial, antifungal, anti-oxidant, anti-allergic, antiinflammatory, anti-thrombotic, hepatoprotective, anti-viral, anticarcinogenic activities. So, this study involved the biological estimation of N’-(3-(hydroxyimino) butan-2-ylidene)-2-oxo-2Hchromene- 3-carbohydrazide (H2L) and its metal complexes.

From this point of view, as a result of the most recent studies conducted in the Institute of Chemistry of Additives of the Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences, it was determined that, biocide additives synthesized at the institute shows biological (physiological) activity in other areas too, in addition to protect the oil products from the microbiological damage. For instance, amino ethanol and some derivatives of amino alcohols synthesized by the employees of Institute shows the properties of anesthetic and terminal anesthesia for the mucous membranes of the eye. The studies were conducted at the first Moscow State Medical Institute named after Sechenov IM. These substances are 7 times greater compared to the widely-used “xycain”, according to its activity.
Bio-oil is a complex mixture which contains a large number of organic compounds, including alcohol, organic acids, phenol, aldehyde, ketone, etc. Some of these chemicals, such as phenols are important industrial raw materials and additives. The total amount of phenolic compounds in the pyrolysis oil varies from 20.0% to 30% depending on the biomass used and operating conditions. Biooil contains several hundreds of chemicals as a result, it exhibits some inferior properties, such as high water content, high oxygen content, high viscosity low flash point, and strong corrosiveness. These drawbacks make it difficult to be directly used as a vehicle fuel.
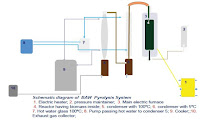
Therefore, several upgrading technologies have been developed to improve the quality of bio-oil, including catalytic hydrodeoxygenation, catalytic cracking, steam reforming, catalytic esterification, supercritical upgrading and so on. Compared with phenols derived from petroleum fuel, these phenolic compounds are renewable and easily obtained. These phenols are not only used as a replacement for phenol in phenol–formaldehyde resins but also as raw materials for developing bio-based antioxidants and many other purposes. Pyrolysis offers the cheapest route to renewable liquid fuels. Nonetheless, many aspects of the pyrolysis pathway are still under investigation.
Ethiopia is the largest livestock producer in Africa, with 70.79 million heads of cattle, 28.48 million sheep, 25.91 million goats, 24.56 million donkeys, 11.39 million horses, 8.08 million mules, 8.39 million camels, and 42.51 million poultry. The largest livestock were found in Oromiya, Amhara and South Nations and Nationalities of People regions. However, the production of livestock is low due to technical constraints to livestock development like absence of approved livestock policy, lack of rural infrastructure and services, inadequate specialists and skilled staff, feed constraints, prevalent animal diseases, grazing land shortage, lack of credit, poor management, low genetic quality of most indigenous breed, recurrent drought, and lack of technical skill on feeding.
While
mass spectrometry has been widely used for decades in biomolecules analyses,
the story of mass spectrometric characterization of nanoparticles (NPs) is
still short. The mass spectrometry has recently received much attention in the
nanoparticle world due to its powerful usefulness especially in elucidating the
chemical structures of the smaller-sized NPs (<5 nm). We are witnessing the
major improvements of mass spectrometry that are taking places both in thestructural analyses of NPs but also in the mass elucidation of NPs. The
advances are mainly coming in the form of improvements in instruments such as
advances in ion sources.

Among the most basic
criterions of a mass spectrometric technique, the two important factors are the
resolution and the sensitivity, of which the former one is increasingly
important in identifying the accurate chemical structures of NPs, and the laterone is of super significance in elucidating the exact mass of NPs. This need
for developing mass spectrometric techniques with better resolution and higher
sensitivity and searching for pathways to improve was noted in some important
research of the leaders in this field.
In the last decade, there has been a phenomenal advancement in theoretical inorganic chemistry, much faster computers are available and commercial programs incorporating the latest methods have become widely available and are capable of providing more information about molecular orbitals (MOs), with a sample input of chemical formula. The focus of attention has been on computational transition-metal chemistry. This is largely due to the successful employment of gradient corrected density functional theory in calculating molecules, particularly of the heavier atoms and in the use of small-core relativistic effective core potential which set the stage for calculation of geometries, bond energies, and chemical reaction and other important properties of transition metal compounds with impressive accuracy.

Application of density functional calculation to organometallic and transition metal compounds is growing. density functional parameters such as eigenvectors, eigenvalues and population analysis are well calculated with this method. In this paper present the calculations of eigenvectors, Eigen values and population analysis of ferrocene and cobaltocene in order to study the extent of contribution of 3d, 4s and 4p orbital in the formation of MOs. Such a quantitative study will provide correct information about the involvement of 4p orbital of Iron and cobalt in bonding will help to resolve the controversy raised by other workers.
Finding newer drugs is an inevitable part of the drug discovery process and nature has proven to be an invincible source for this purpose. Phytoconstituent anaylsis has always been an integral part of drug discovery process for finding newer molecules with therapeutic efficacy that can be used for the treatment of various diseases and ailments. The lead of such compounds may come from the available traditional knowledge or by the randomized pharmacological or biological screening of the crude drug extracts.
 Phytoconstituent analysis involves usage of various analytical techniques for the isolation and characterization of phytoconstituents. Primitive techniques basically involved usage of column chromatography for the purpose of isolation of phytoconstituents wherein silica used to act as stationary phase and mobile phases ranges non-polar to polar solvents. Though this technique was highly beneficial but had several drawbacks such as longer time periods and isolates obtained were not highly purified. Later on, flash chromatography was introduced wherein pressurized gas was used to drive the solvent through the column of stationary phase resulting in a rapid and high resolution chromatography.
Phytoconstituent analysis involves usage of various analytical techniques for the isolation and characterization of phytoconstituents. Primitive techniques basically involved usage of column chromatography for the purpose of isolation of phytoconstituents wherein silica used to act as stationary phase and mobile phases ranges non-polar to polar solvents. Though this technique was highly beneficial but had several drawbacks such as longer time periods and isolates obtained were not highly purified. Later on, flash chromatography was introduced wherein pressurized gas was used to drive the solvent through the column of stationary phase resulting in a rapid and high resolution chromatography.
Advances in biotechnology have provided a wide range of therapeutically active and commercially available biologic large molecules as protein and peptide drugs. However, oral administration of these drugs has been highly limited due to the stability and the difficulties to cross the gastrointestinal membrane. Significant research attempts have been made in recent years to utilize carrier-mediated transport systems for enhancement in the oral bioavailability. Among various intestinal transporters, the intestinal bile acid transporter has a good potential because of its higher capacity and low structural selectivity. The transport system facilitates the daily absorption of 10-20 g bile salts at a more than 95% efficiency rate.

The system also tolerates significant chemical modifications at the C3 and C24 positions of the sterol nucleus. Thus, the intestinal bile acid transporter has been specifically investigated for its ability to increase the oral absorption of cholic acid conjugates of proteins and small peptides through the carrier-mediated transport mechanism. The fact that the bile acid transporter tolerates the chemical modifications of cholic acid provides a solid rationale for the development of a cholic acid-peptide conjugate for enhanced oral absorption.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are large group of organic compounds with two or more fused aromatic ring. These compounds are solids with low volatility at room temperature. They are relatively insoluble in water and most can be degraded to simpler substances. Regulatory agencies such as US environmental protection agency (EPA) and agency for toxic substances and disease registry (ATSDR) have defined maximum allowable level of PAHs in the environment due to their adverse health effect to human. Exposure to PAHs can occur from different sources such as water, food and air. Incense burning is associated with many culture and ceremonies in many countries.

The incense materials are used to fragrant the environment and most of the people do not know that this fragrant may cause indoor air problems. Different carcinogenic substances have been detected in incense smoke. The exposure to incense smoke have been found to make lung cancer, asthma, headache, nausea and allergic to skin and eyes. One of the suggestions to prevent lung cancer in the community should include the reduction or minimization of exposures to indoor air pollutants. Beside PAHs, incense burning was found to be the significant source of particulates, heavy metals and volatile organic compounds.
Metals are found in different forms in nature. One of the major forms is a molecule resulted from the coordination of metals with other molecules or ions. Such associations are often referred as coordination complexes. These coordinated complexes play very important roles in the physiological activities of human and plant lives. For example, haemoglobin, a macromolecule responsible for the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood, consists of coordination of iron with nitrogen bases around it. Oxygen is transported by the first coordination sphere of the complex, whereas CO2 is transported by the second coordination sphere of the iron complex called heme. In plants, photosynthesis is carried out by the pigments called chlorophyll where coordination of magnesium with other molecules plays a vital role. Such prevalence of metal complexes indubitably make them a wide branch of study. The transition metal complexes are rich in structural diversity.
![Natural Bond Orbital Analysis of [Fe(H 2O)6]2+/3 Natural Bond Orbital Analysis of [Fe(H 2O)6]2+/3](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj0aguGiPaQgpOaJAO2idqOUorZdpSOzln7FRTVxUFkMwZ1HldHAgTd6pfM6u_Y3E262R1eyCMA20RADpkurhEuJsY1QSSBFi8whqGSVVOpe-1-AbGl0l2iLQRGsSjcoULeZ_vrktYeSTCu/s200/Natural+Bond+Orbital+Analysis+of.png)
Many successful computational study of aqua complexes have validated the outcomes of ab-initio methods using density functional theory. Structure and vibrational properties of the complexes [Fe(H2O)6]2+ and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ have been fastidiously studied by Jarzecki and co-workers with DFT approach. The geometries of the complexes are precisely determined computationally at B3LYP level of approximation. With the same DFT approach the aqua complexes of Zn2+ ion have been studied by Rul´ısekˇ and Havlas.
Famotidine (FAM), 3-[({2-[(diaminomethylidene) amino]-1,3- thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]-N’- sulfamoylpropanimidamide, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is commonly used in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease. The chemical formula of FAM together with the atomic numbering . Due to the presence of amino, amido and thioether groups in its structure, this drug possesses chelating properties and may interact very effectively with the essential metal ions present in blood plasma and different tissues. In the crystalline state, famotidine has two polymorphic forms that differ by arrangement of intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
 Several binary FAM complexes containing divalent transition metal ions have been synthesized in solution as well as in the solid state. Determination of stability constant of complexes with drugs are useful to know the proper dose of drug and their effect with all other components of blood stream as well as to measure the strength of metal ligand bonds. The complexes of drugs have higher efficacy than parent drugs. In the present investigation, the stability constants of zinc (II) complexes with famotidine(FAM) and peptides (L) were studied in detail by potentiometric titration method in aqueous solutions at 25°C and I=0.10 mol/L NaNO3. Species distribution over a range of pH of the complexes in solution was evaluated.
Several binary FAM complexes containing divalent transition metal ions have been synthesized in solution as well as in the solid state. Determination of stability constant of complexes with drugs are useful to know the proper dose of drug and their effect with all other components of blood stream as well as to measure the strength of metal ligand bonds. The complexes of drugs have higher efficacy than parent drugs. In the present investigation, the stability constants of zinc (II) complexes with famotidine(FAM) and peptides (L) were studied in detail by potentiometric titration method in aqueous solutions at 25°C and I=0.10 mol/L NaNO3. Species distribution over a range of pH of the complexes in solution was evaluated.


























![Natural Bond Orbital Analysis of [Fe(H 2O)6]2+/3 Natural Bond Orbital Analysis of [Fe(H 2O)6]2+/3](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj0aguGiPaQgpOaJAO2idqOUorZdpSOzln7FRTVxUFkMwZ1HldHAgTd6pfM6u_Y3E262R1eyCMA20RADpkurhEuJsY1QSSBFi8whqGSVVOpe-1-AbGl0l2iLQRGsSjcoULeZ_vrktYeSTCu/s200/Natural+Bond+Orbital+Analysis+of.png)

