Coronary
Artery Disease (CAD), cancer, stroke, pulmonary diseases, obesity, and other
pathologies related metabolic syndrome are the leading causes of mortality and
morbidity in the modern world. Some biologic markers are associated withincreased risk for these diseases. Insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, increased
activation of the coagulation cascade, elevations in cell adhesion molecules
and in molecules associated with inflammation play important role in
pathogenesis of these diseases. High blood levels of Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)]
has been identified as a risk factor for cerebrovascular disease (CVD),
atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and stroke.
Heavy metals pollution arises from different sources in the result of industrial actions and scientific improvement but most commonly is due to purification of metals. Discharge of the Heavy metals in the water bodies because of Anthropogenic actions is most important water pollution source. Co, Zn, Cu, Ni, Pb, Hg, are frequently detected in engineering wastewaters, which instigate as of metal plating, mining activities, smelting, battery construct, tanneries, oil refining, smear manufacture, pesticides, dye manufacture, printing and picturesque industries, etc.. Heavy metals must be removed before discharge because unlike organic wastes, heavy metals are non-biodegradable and build up in gulp of air tissues, and responsible for various diseases and disorders. Cobalt is an odorless, steely-gray, shimmering, rigid metal.
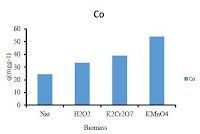 Everyone is unwrapping to the fundamentals to small levels of Cobalt in atmosphere, stream and foodstuff. 2 gdm³ of Cobalt in consumption water has been estimated. Cobalt has both advantageous and destructive special effects on physical condition. Important natural sources of Cobalt in the atmosphere are loam, grime and marine irrigate. The sensitive Co (II) poisoning cause dangerous health hazards in humans like asthma, failure of heart, harm to liver and thyroid.
Everyone is unwrapping to the fundamentals to small levels of Cobalt in atmosphere, stream and foodstuff. 2 gdm³ of Cobalt in consumption water has been estimated. Cobalt has both advantageous and destructive special effects on physical condition. Important natural sources of Cobalt in the atmosphere are loam, grime and marine irrigate. The sensitive Co (II) poisoning cause dangerous health hazards in humans like asthma, failure of heart, harm to liver and thyroid.

Additionally, there is much interest in the
anticancer activity of these compounds owing to different types of biological
targets they might interfere with for this effect to occur e.g., PDE3, PIM1
Kinase, and Survivin protein. In view of the previous applications andcontinuation of our previous work on chemistry and pharmaceutical activity on
nicotinonitrile derivatives we aim to use
4-methyl-2,6-dioxo-1-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3- carbonitrile as
building blocks for the synthesis of some new family of fused heterocyclic
compounds incorporating pyridine moiety with the hope to possess better
anticancer activity.
The fundamental role and effects of enzymes in the key processes of DNA replication and transcription have been deeply addressed during the last ten years. In fact, it is well established nowadays that the initiation of DNA transcription is tributary to the synthesis of the polymerase-RNA which is known as the main factor contributing to break the strong hydrogen bonds linking bases in pairs, for the genetic code to be exposed out of the stack. Unlocking the complexity of such a phenomenon has then been shown to mainly depend on the DNA complex structure, as it requires, among the numerous involved degrees of freedom, the unwinding of the double helix. That complexity mainly comes from its structure which is primarily made of random distributions of four types of bases, adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and Guanine (G). Besides, the pairing of the bases respects a universal complementarity where A can bind only to T and C to G.

The bases are put together by hydrogen bonds, and the AT pair contains two H-bonds while the GC pair contains three of them. Among the models introduced to describe the dynamics of such a complex molecule, the Peyrard-Bishop (PB) model has been extensively used in the last ten years because of its capability of predicting the occurrence of denaturation bubbles as widely observed in experiments where the so-called first-order phase transition emerges. Furthermore, many studies have been carried out, showing that it support solitonic structures and is rather suitable to observe the localization of the energy which drives the key dynamical processes known as replication and transcription.
There
has been considerable interest in the development and usage of plant based
natural coagulants. The use of plant-based materials as water treatment agents
has long history, particularly the wood charcoal as an excellent adsorbent.
Natural polyelectrolyte of plant origin has been used for many centuries indeveloping countries for purification of turbid water. For home water treatment,
the plant-based materials have been used in the forms of powder and paste, 90%
of which consists of substances other than the polyelectrolytes. Even under
such conditions, few plant seeds make effective coagulants. Several plant-based
materials were identified as a natural coagulant such as Moringa (Malunggay),
Strychnos (Clearing nut tree) and Cactus.
There has been enormous report directed towards the development of novel chemical compounds able to arrest or reverse the development of cancer. Biological activities of transition metal complexes derived from Schiff base ligands are one of the most exhaustively studied topic in coordination chemistry, due to their enhanced activities compared to non - Schiff base complexes. Schiff base complexes show important physiological and pharmacological activities due to their favorable cell membrane permeability. For example, amino acid Schiff base metal complexes have a wide variety of applications including biological, clinical analytical and industrial area in addition to their important role in catalysis and organic synthesis.
The toxicity of free heme has been documented in several
disease types. For example, in hemolytic anemias such as sickle cell disease
and thalassemia, release of heme from hemoglobin following lysis of red bloodcells is known to cause cell death. In a critical care situation such as
hemorrhagic injury, neuronal cell death is caused by the lysis of red blood
cells, which release hemoglobin and its breakdown product hemin. Physiological
levels of free heme in the blood are maintained at low levels (0.1 -1 μM) by
the high binding affinity of proteins such as serum albumin, hemopexin and
haptoglobin.
Calcareous soils have resulted in precipitation of CaCO3
from water of some rivers which contain high amount of CaH(CO3)2. The tropical
aridity creates reaction resulting in accumulation of salts. Most of the waterof uplands is lost due to runoff and transpiration reducing effective leaching.
Precipitation of calcium increases sodium concentration which is further
augmented by high RSC of the available water resources. Salinity is the major
yield reducing factor in legume cultivation as legumes are salt sensitive crop,
especially in the seedling stages where they are most susceptible to damage due
to water stress and ion-imbalance.

In saline soils, many environmental factors
such as soil pH, water deficiency and nutrient deficiency are reported in
Ref.that the seedling stage suffers most damage due to ion-imbalance and thus,
other physiological processes are negatively affected during the growth of theplant especially photosynthesis. Ref.reported that during long term exposure to
salinity, plants experience premature senescence of adult leaves and root
nodules which reduce the net photosynthetic area available to support continued
growth of the plant. Thus, bio-synthesis of sugar and nitrogen fixation are
negatively affected.







